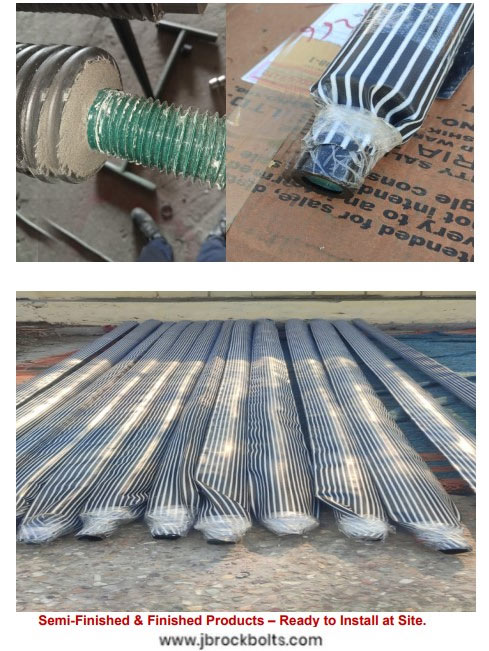
JB-10 S.N. Bolts - Soil Nails - DCP Anchors
JB Engineering Soil Nailing Bolts are used in various Hydro Power Projects, Road Projects and Projects of the similar nature to provide strength and durabilty FUSSION BONDED EPOXY COATED & GALVANIZED MATERIALS AVAILABLE as well.
Rock bolts are 15 to 32 diameter bars, inserted in 30 to 60 mm bore holes. They are generally between 3 and 6 meters long. Let’s explore the various types of rock bolts and how they are used to ensure a secure structure.

Soil Nailing bolts usually involves the insertion of reinforcement bars (Hollow/solid) into the exposed slope followed by grouting, placement of a wire mesh and shotcreting before the testing and locking off of the nail through stressing jacks. Hollow soil nail bars can also be self-drilling thus acting as drilling rods with expendable drill bits. Soil nails are cost effective for stable soils where water pressure is not an issue and for excavations where space is a constraint.
They may be bonded along their entire length by cement grouting or anchored at various points at the base of the hole using chemical resin or a mechanical anchorage. Rock bolts transfer load from the unstable exterior, to the confined (and much stronger) interior of the rock mass.

SOFT GROUND: SOIL NAILS
Applying the principles of systematic rock anchoring to soil seems to be obvious, but the requirements for soil nailing are higher. Soil nails are 20 to 50 mm diameter bars, inserted in 70 to 150 mm bore holes. They are generally over 6 meters long and may be as much as 30 meters.
A SOIL NAILING ANCHOR BOLTS CONSISTS OF:
- Stabilization of excavations
- Embankment stabilization
- Stabilization and renovation of land slips
- Road construction
- Extension Couplings
SOLID BAR AND HOLLOW BAR
These two techniques above insert the reinforcing element (reinforced concrete) into the soil/rock mass. The solid and hollow bars both are available in JB Engineering Rock Bolts, India. Solid bars are usually installed into the pre-drilled holes and then grouted into place using a separate grout line, whereas hollow bars may be drilled and grouted simultaneously by the use of a sacrificial drill bit and by pumping grout down the hollow bar as drilling progresses. Applying for underground applications in unconsolidated soil/rock conditions, hollow bar is typically effective.
INSTALLATION OF SOIL NAIL:
- Inserting Bar
- Spraying Shotcrete
- Applying Plate
- Road construction
- Spraying Shotcrete

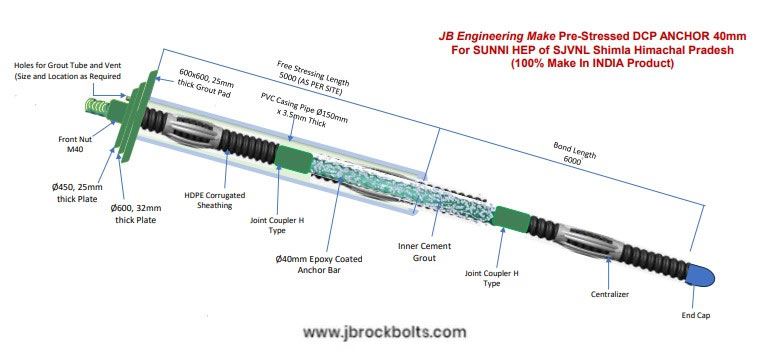
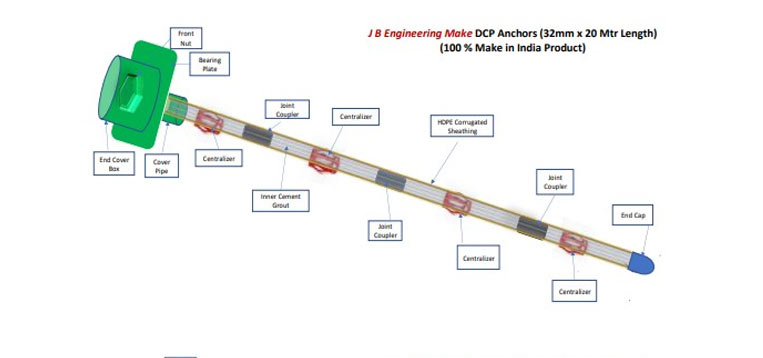
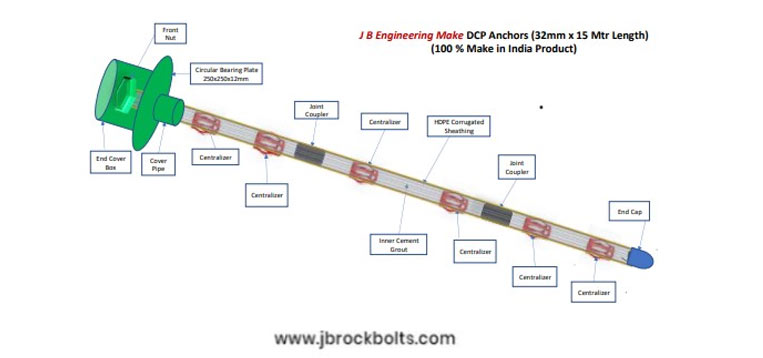
JB Engineering DCP-Anchors
JB Engineering’s Double Corrosion Protection (DCP) Anchors are HOT DIP ZINC Coated & Fusion EPOXY COATED which provides protection from Corrosion for minimum 100 Years with two independent barriers between the anchor tendon and the environment. Grouted corrugated sheathing with controlled crack width and are for permanent use. Mostly used in high rise construction for heavy reinforcement.
- Ground anchors are unique as they can provide active restraint to the structures.
- Anchors avoid movements by applying a compressive load to a structure.
JB Engineering’s (DCP) - DOUBLE CORROSION PROTECTION Anchors classifies as like below:
- The application of ground anchors is increasing as they enable construction in densely populated areas. This increase is due to the reductions in available space for traditional construction methods.
- In areas of limited easement, removable anchors can be used. For projects where further underground construction, like adjacent developments of tunnels is anticipated engineers can use resized anchors produced from composite materials.
Features of DOUBLE CORROSION PROTECTION Anchors are:
- Hot Zinc Coated / Fusion Epoxy Coated anchors provide minimum 100 Years Corrosion Protection.
- Bond length and free length to enable pre-stressing.
- Capacities: bars 4,500 kN, strand15,900 kN(+)
- Anchors with diameter range12-75mm strand anchors up to 63mm(+)
- Full compatibility with infrastructure intelligence, utilizing multiple sensor types.
How ground anchors work: - JB Engineering Pre-stressed grounds Double Corrosion Protection (DCP) Anchors are HOT DIP ZINC Coated & Fusion EPOXY COATED provides protection from Corrosion for Minimum 100 Years & more actively contribute to the stability of a structure throughout its design life. The performance of the anchor is critical to the stability of the structure.
Stressing jacks are used to pre-stress the anchor and elongate the tendon. Once the necessary load has been established, the anchor is locked off at the head. The anchor then applies a compressive load to the structure to arrest movement.
The anchor is un-bonded from the ground between the structure and the load-bearing strata to prevent load from being transferred in to unsuitable material and to ensure that sufficient elongation of the tendon is possible. Upon reaching the desired depth, the tendon is directly bonded to the ground, forming the two fundamental elements of the ground anchor: the free length and the bond length.
In permanent work, anchors need to be protected against corrosion in line with internationally recognized anchor design standards. Double corrosion protection (DCP) is provided with HOT DIP ZINC coating process & fusion EPOXY COATED process which provides protection from Corrosion for Minimum 100 years with two independent barriers between the anchor tendon and the environment.
Introducing JB Engineering Smart Technologies:
JB Anchors are the first in a series of smart products developed by JB Engineering.
THIS TYPE OF ANCHORAGE SYSTEM IS USED AS A PERMANENT ANCHOR.
- Used as a permanent anchor, which means last for a long duration. (up to 100 years).
- Encapsulations, corrugated sheathing is used in both unbonded and boned length portions.
- Double corrosion protection is achieved by using both encapsulations with strands that are greased and are individually protected.
APPLICATIONS:
- Uplift control
- Toe stabilization
- Rock stabilization
- Positional stability